Developing An Ideology: Evolution Of The Pakistani Taliban – Analysis

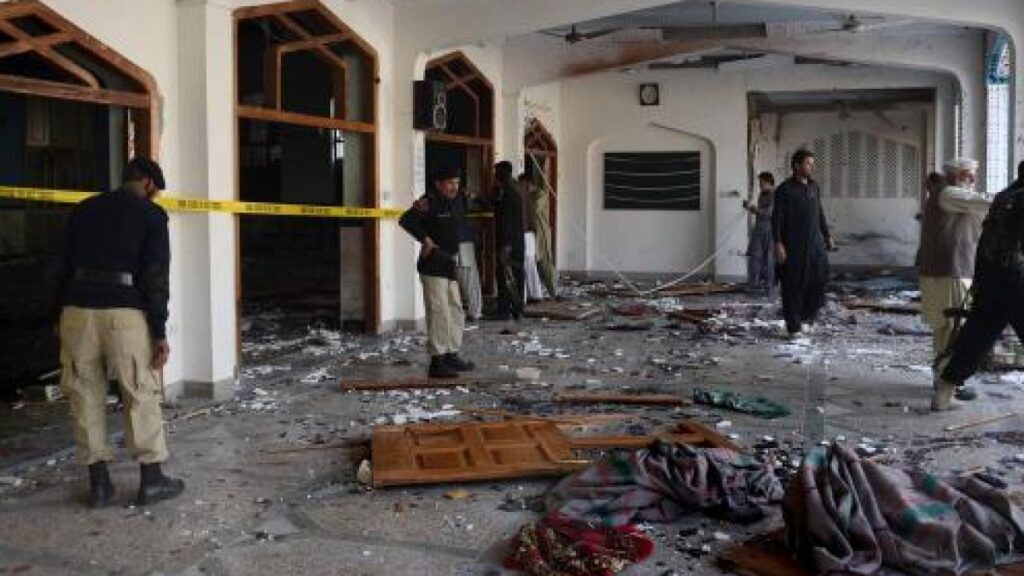
The militant outfit, Tehreek-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP), has been at the heart of several attacks in Pakistan lately. Most recently, it has been accused of the explosion in a mosque in Peshawar at the end of January 2023, which killed over 100 people. These attacks point to the TTP gearing up for an ideological battle, which could see the introduction of a fresh component to the South Asian militant terrain.