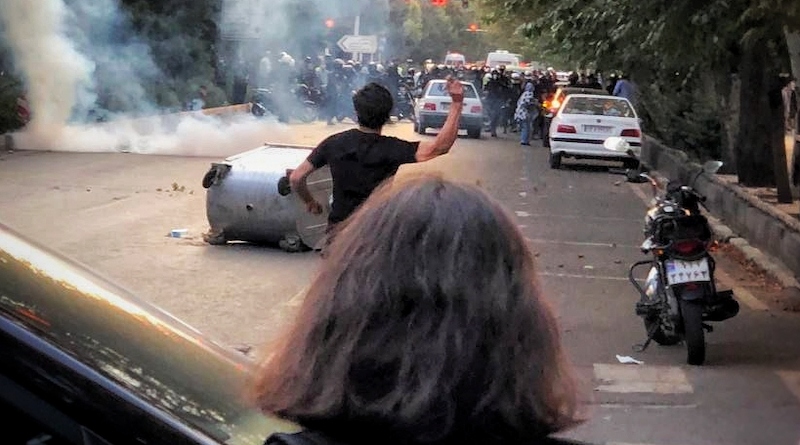More than a month ago, “morality police” in Tehran accosted 22-year-old Mahsa Amini over the arrangement of her mandatory head covering, subjected her to such physical abuse that she fell into a coma and died three days later. Since then, international media have attached ever greater significance to the ensuing protests but have repeatedly fallen into the trap of undermining that perception with descriptions of the protests as “leaderless.”
That label clearly gives the impression that the uprising is also aimless, that there is no precise or unified ambition behind it, and that it is primarily just an expression of general outrage over Ms. Amini’s death at the hands of abusive authorities. In reality, the uprising moved beyond the issues of forced veiling and violent enforcement of religious behavior long ago. Its emphasis today is much broader, and its message conveys very specific demands for systemic change and the ouster of Iran’s existing clerical leadership.
Since the initial round of protests grew out of Ms. Amini’s funeral on September 17, the movement has expanded to encompass at least 190 cities spanning all 31 provinces. It has also seen continuous participation from a wide range of ethnic and religious groups, professions, class backgrounds, and ages. At the start of October, teenagers became a prominent force within the movement, as students in high schools began protesting and chanting “Death to Khamenei,” referring to the regime’s Supreme Leader, Ali Khamenei.
Later in the month, the movement acquired a strong economic component, with oil industry workers staging protests explicitly to express solidarity with the nationwide uprising. At the site of their strikes, the workers were heard repeating the same slogans that have defined the current uprising and several prior nationwide protest movements. Chief among these is “death to the dictator,” “Death to Khamenei,” and “Death to the oppressor, be it the Shah or the Leader (Khamenei).”
Additionally, protesters throughout the country have been heard to publicly embrace a message of self-sacrifice that reflects an accompanying increase in the rate of direct clashes between security forces and civilians.
It is difficult to imagine people all across Iran chanting, “We will fight, we will die, but we will reclaim Iran,” if those people do not believe themselves to be unified behind a specific goal with an established leadership and a network that leads the protests and its slogans all across Iran. Indeed, it is absurd on its face to suggest that the message of these protests could swiftly come into nationwide alignment and remain aligned for more than a month without significant leadership and organization behind them. The slogans and actions that have been established by the MEK Resistance Units in the past five years.Unfortunately, such claims are par for the course when it comes to international media coverage of Iranian affairs. Even more, unfortunately, such coverage has contributed to the widespread perception within Western policy circles that there is no viable alternative to Iran’s theocratic dictatorship. This, in turn, has encouraged a longstanding trend of wrong-headed policies for dealing with the Iranian regime – policies that arguably rise to the level of appeasing the Iranian regime while continually marginalizing the Iranian people.
To their credit, Western journalists and policymakers have appeared increasingly open to the notion that the current uprising could set the stage for a new revolution and ultimately lead to the mullahs’ ouster. But as they continue coming to terms with that idea, the same journalists and policymakers must make stronger efforts to understand precisely where that revolution will lead.
There are several Western policymakers who have long since acquired that understanding. In the United States House of Representatives, there are at least 260 of them who have endorsed a resolution affirming the Iranian people’s right to oppose tyranny and expressing support for the leading pro-democracy opposition group, the People’s Mojahedin Organization of Iran (PMOI/MEK). The MEK has played an unmistakable role in this and several prior uprisings that gave voice to public demands for regime change and a democratic alternative.
No less an authority than the regime’s Supreme Leader Khamenei acknowledged the MEK’s role in January 2018, when Iran was in the midst of another series of protests – the first of several to feature explicit condemnation of the entire system on a national scale. Since then, the MEK’s network of “Resistance Units” has continually grown more active, broadening its tactics to include the defacing and shutting down government websites and state media broadcasts alongside the destruction of government billboards and statues and the posting in public spaces of pro-democracy messages and images of Maryam Rajavi the President-elect of National Council of Resistance of Iran and Massoud Rajavi, leader of the Iranian resistance.
The 10-point plan of Maryam Rajavi for the future of Iran and the MEK’s platform is well-known to Iranians, especially young Iranians, who have made a regular habit of evading the regime’s restrictions on access to the internet and independent media. Thus, whether made explicit in protest gatherings or not, it is clear that the MEK’s vision is the vision that most Iranians are pursuing whenever they band together to chant “Death to the oppressor, be it the Shah or the Leader (Khamenei).”