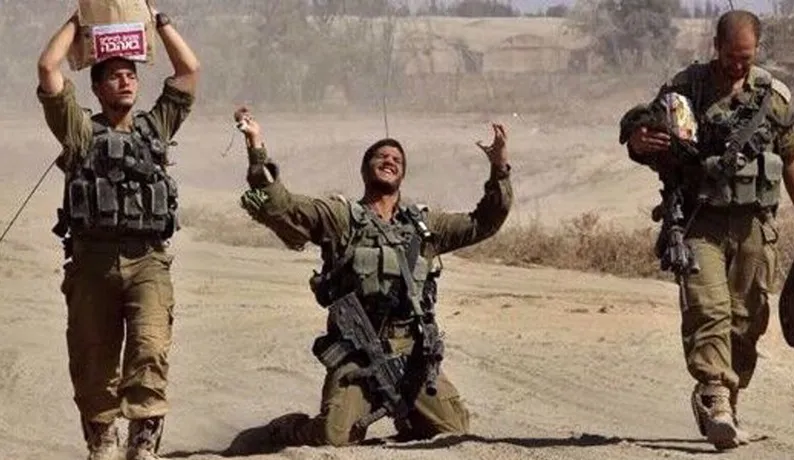
Gallant: Hezbollah fired over 1,000 munitions at Israel since start of war with Hamas
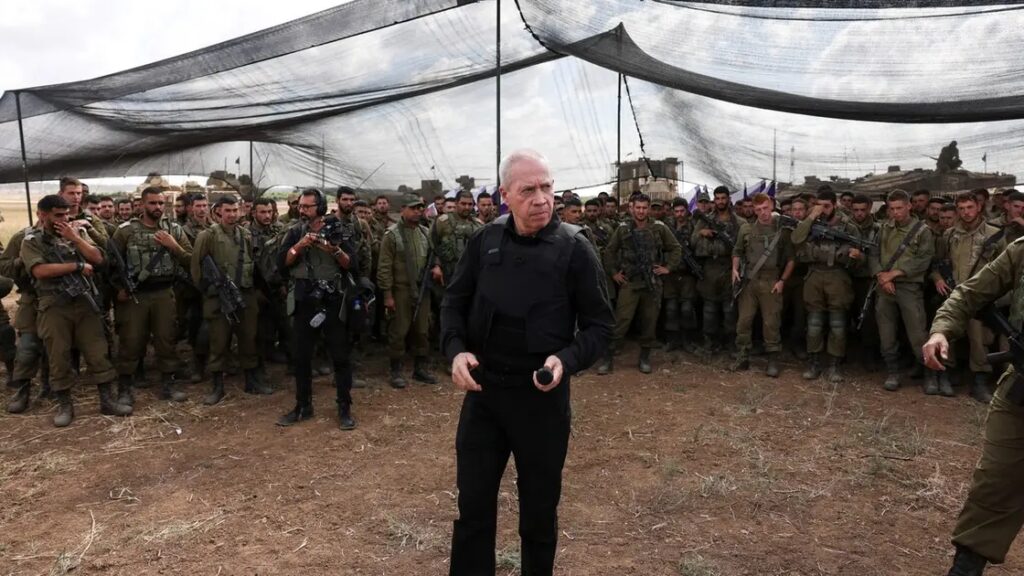

Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant said that Lebanon’s Iran-backed Hezbollah had fired 1,000 munitions at Israel since October 7 when the Israel-Hamas war broke out in Gaza, and warned that Tehran was increasing its attacks against Israel.