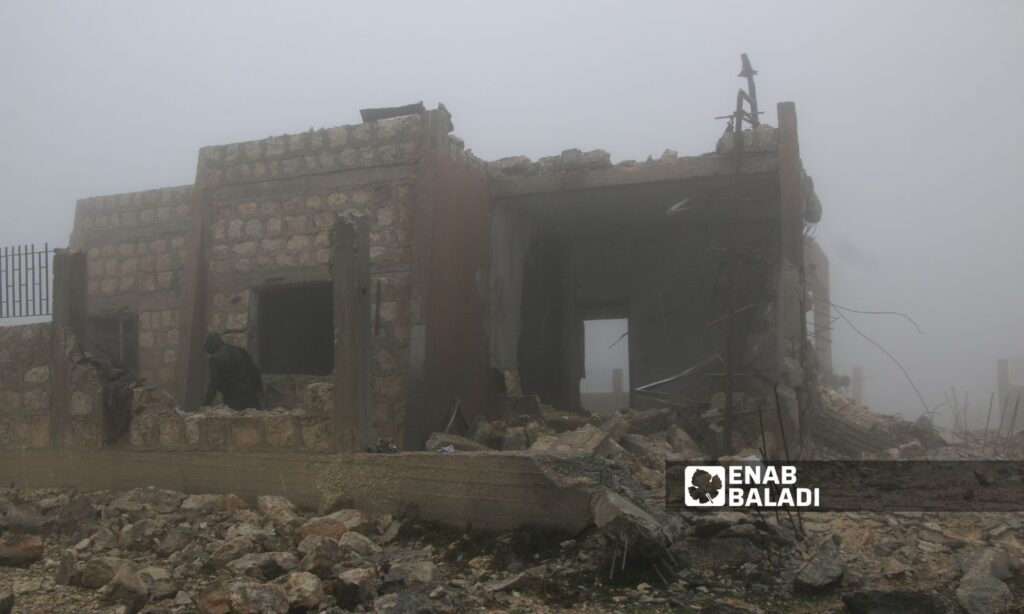
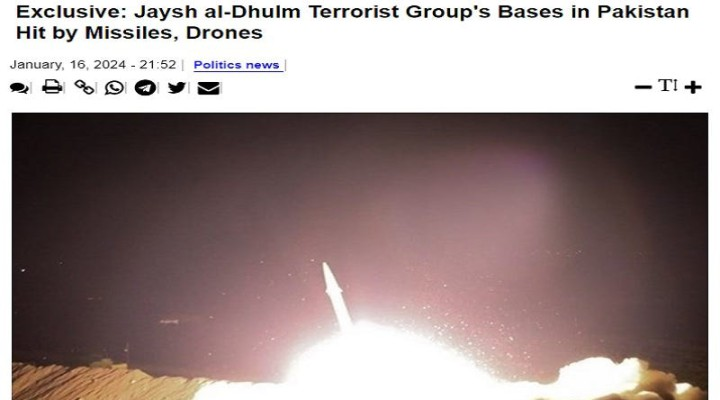
The battle to save Jerusalem’s Armenian Quarter

In-depth: Armenian lawyers and the diaspora community in Jerusalem are uniting their efforts to push back against secretive Israeli land deals.
Yerevan, Armenia – There are mounting concerns in Armenia regarding a controversial land lease agreement in East Jerusalem’s Armenian Quarter, with many fearing the issue goes well beyond just a commercial deal.